| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
- Model Serving
- knative
- Pulumi
- argocd
- Kubeflow
- kubernetes operator
- nginx ingress
- blue/green
- Kopf
- Kubernetes 인증
- xdp
- keda
- operator
- 카오스 엔지니어링
- eBPF
- seldon core
- gitops
- opentelemetry
- CI/CD
- CANARY
- Litmus
- Argo
- serving
- MLflow
- mlops
- opensearch
- tekton
- Continuous Deployment
- Kubernetes
- 오퍼레이터
- Today
- Total
Kubernetes 이야기
jenkins 를 활용하여 Kubernetes에 이미지 배포 및 모니터링 본문

Jenkins는 소프트웨어 개발 시 지속적 통합(CI) 서비스를 제공하는 툴로써 대시보드,Pipeline, 다양한 플러그인 등을 지원한다.
Jenkins는 Kubernetes환경이 나오기 전부터 사용되던 툴로 PC 또는 VM 환경에 설치하여 운영을 많이 해 왔고, 다양한 플러그인을 제공, Groovy Script를 기반으로 다양한 프로세스를 만들 수 있다는게 장점이다.
이번 글에서는 Jenkins를 Kubernetes의 Pod로 실행하고, Container image build 후 Kubernetes에 Deploy하는 절차를 알아보자.
Jenkins는 Master 단독으로도 CI/CD 환경을 구축할 수 있지만, 빌드하는 프로젝트가 많은 경우 Master / Slave 구조로 운영한다.
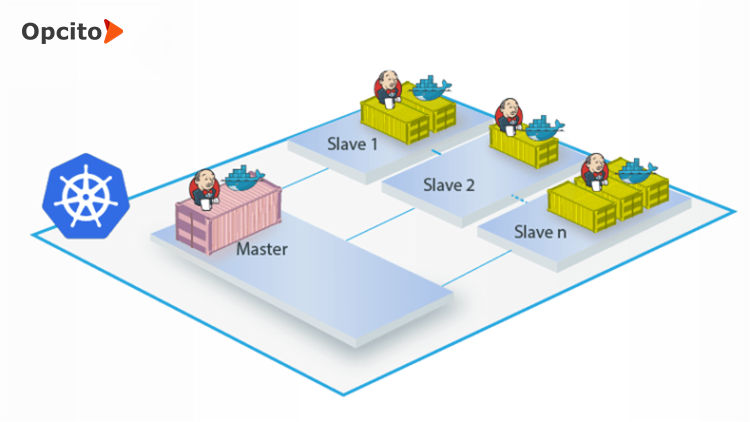
Jenkins설치는 크게 3가지 방법이 있다.
- Helm (v3) 설치 방법
- Yaml 설치 방법
- Jenkins Operator를 이용한 설치 방법
이번에는 Helm 으로 설치를 진행해 보자.
설치
$ kubectl create namespace jenkins# helm repo add jenkinsci https://charts.jenkins.io
# helm repo updatehelm 설치 전 먼저 jenkins volume을 먼저 생성하자.
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: jenkins-pv
spec:
capacity:
storage: 8Gi
volumeMode: Filesystem
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Delete
local:
path: /data/jenkins
nodeAffinity:
required:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: kubernetes.io/hostname
operator: In
values:
- node1apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: jenkins-pvc
namespace: jenkins
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 8Gi
volumeMode: Filesystem이제 jenkins라는 service account를 생성한다.
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: jenkins
namespace: jenkins
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
annotations:
rbac.authorization.kubernetes.io/autoupdate: "true"
labels:
kubernetes.io/bootstrapping: rbac-defaults
name: jenkins
rules:
- apiGroups:
- '*'
resources:
- statefulsets
- services
- replicationcontrollers
- replicasets
- podtemplates
- podsecuritypolicies
- pods
- pods/log
- pods/exec
- podpreset
- poddisruptionbudget
- persistentvolumes
- persistentvolumeclaims
- jobs
- endpoints
- deployments
- deployments/scale
- daemonsets
- cronjobs
- configmaps
- namespaces
- events
- secrets
verbs:
- create
- get
- watch
- delete
- list
- patch
- update
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- nodes
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- update
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
annotations:
rbac.authorization.kubernetes.io/autoupdate: "true"
labels:
kubernetes.io/bootstrapping: rbac-defaults
name: jenkins
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: jenkins
subjects:
- apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Group
name: system:serviceaccounts:jenkinshelm 설치 시 필요한 values.yaml 을 https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jenkinsci/helm-charts/main/charts/jenkins/values.yaml 에서 다운 받아 아래의 내용을 수정한다.
- serviceType: NodePort
- existingClaim: jenkins-pvc
- storageClass:
- serviceAccount:
create: false
name: jenkins이제 jenkins를 실행해 보자.
# helm install jenkins -n jenkins -f jenkins-values.yaml jenkinsci/jenkins
NAME: jenkins
LAST DEPLOYED: Thu Sep 8 16:45:08 2022
NAMESPACE: jenkins
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
NOTES:
1. Get your 'admin' user password by running:
kubectl exec --namespace jenkins -it svc/jenkins -c jenkins -- /bin/cat /run/secrets/additional/chart-admin-password && echo
2. Get the Jenkins URL to visit by running these commands in the same shell:
export NODE_PORT=$(kubectl get --namespace jenkins -o jsonpath="{.spec.ports[0].nodePort}" services jenkins)
export NODE_IP=$(kubectl get nodes --namespace jenkins -o jsonpath="{.items[0].status.addresses[0].address}")
echo http://$NODE_IP:$NODE_PORT/login
3. Login with the password from step 1 and the username: admin
4. Configure security realm and authorization strategy
5. Use Jenkins Configuration as Code by specifying configScripts in your values.yaml file, see documentation: http:///configuration-as-code and examples: https://github.com/jenkinsci/configuration-as-code-plugin/tree/master/demos
For more information on running Jenkins on Kubernetes, visit:
https://cloud.google.com/solutions/jenkins-on-container-engine
For more information about Jenkins Configuration as Code, visit:
https://jenkins.io/projects/jcasc/
NOTE: Consider using a custom image with pre-installed pluginsJenkins 관리자 암호
# jsonpath="{.data.jenkins-admin-password}"
# secret=$(kubectl get secret -n jenkins jenkins -o jsonpath=$jsonpath)
# echo $(echo $secret | base64 --decode)이제 NodePort 로 브라우저를 통해 접속해보자.


설치 후 Plugin 업데이트를 진행하여 Kubernetes 및 Pipeline plugin 을 설치하자. ( Kubernetes Plugin 만 별도로 설치해도 된다. )

Build
이제 Git 소스로부터 Container Image를 만드는 과정을 살펴보자.
파이프라인 Script 를 작성하기 전에 현재 Kubernetes 환경이 Docker engine없이 containerd 만 설치되어 있어 docker build 대신 Kaniko로 빌드를 진행하도록 한다. 이 때 Kaniko에서 사용할 Credential을 위해 secret을 먼저 생성하자. ( jenkins에서 만든 이미지를 Dockerhub에 저장하기 위한 계정정보이다. )
kubectl create -n jenkins secret docker-registry docker-credentials \
--docker-username=kmaster8 \
--docker-password='<password>'다음과 같이 pipeline을 생성한다.
pipeline {
environment {
registryCredential = "docker"
}
agent {
kubernetes {
yaml """
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
labels:
jenkins-build: app-build
some-label: "build-app-${BUILD_NUMBER}"
spec:
containers:
- name: kaniko
image: gcr.io/kaniko-project/executor:v1.5.1-debug
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
command:
- /busybox/cat
tty: true
volumeMounts:
- name: jenkins-docker-cfg
mountPath: /kaniko/.docker
volumes:
- name: jenkins-docker-cfg
projected:
sources:
- secret:
name: docker-credentials
items:
- key: .dockerconfigjson
path: config.json
"""
}
}
stages {
stage('Checkout') {
steps {
script {
git url: 'https://github.com/kmaster8/flask-helloworld.git', credentialsId: ''
sh 'ls -la'
}
}
}
stage('build') {
steps {
container('kaniko') {
sh '/kaniko/executor --context `pwd` \
--destination docker.io/kmaster8/helloworld:2.0 \
--insecure \
--skip-tls-verify \
--cleanup \
--dockerfile Dockerfile \
--verbosity debug'
}
}
}
}
}이제 build를 시작하면 dockerhub에 다음과 같이 이미지가 저장되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.

이제 이미지를 배포하였기 때문에 해당 이미지를 Kubernetes에 배포하는 CD과정을 진행해 보자. CD 과정은 ArgoCD 같은 GitOps 도구를 사용할 수 있지만, 여기서는 Jenkins에서 모두 배포까지 진행하는 과정으로 테스트해보자.
Jenkins에서 Kubernetes 에 Yaml을 배포하기 위한 몇가지 방법 중 Continuous Deployment 플러그인을 통해 배포하는 방법을 살펴보자.
우선 Kubernetes는 RBAC 모드로 대부분 운영된다. 그래서 배포를 위해서는 각 권한에 맞는 사용자의 Token ( Service Account ) 값이 필요하다. 이를 Jenkins에 등록하여야 한다.

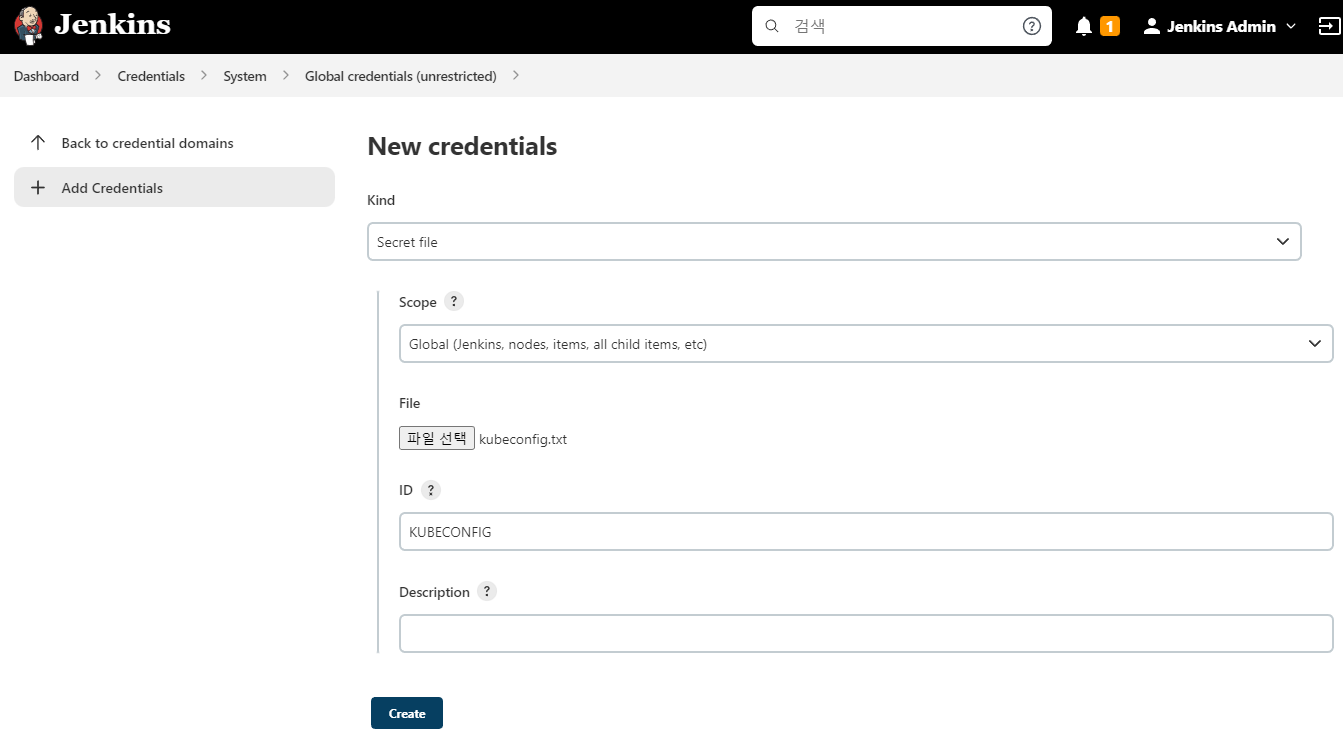
그리고, Kubernetes CLI Plugin을 설치한다.

이제 위의 Pipeline에 다음을 추가한다.
...
containers:
- name: kubectl
image: gcr.io/cloud-builders/kubectl
command:
- cat
tty: true
- name: kaniko
...
stage('deploy') {
steps {
script {
withKubeConfig([credentialsId: 'KUBECONFIG', serverUrl: 'https://kubernetes.default', namespace: 'test']) {
container('kubectl') {
sh 'kubectl apply -f deploy.yaml'
}
}
}
}
}
...deploy.yaml은 다음과 같다.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: hello
labels:
app: hello
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: hello
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: hello
spec:
containers:
- name: hello
image: docker.io/kmaster8/helloworld:2.0
imagePullPolicy: Always
ports:
- containerPort: 5000
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: hello
labels:
app: hello
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 5000
targetPort: 5000
nodePort: 30050
protocol: TCP
name: http
selector:
app: hello이제 빌드를 수행하면 다음과 같이 deployment가 배포된 것을 볼 수 있다.
# k get svc,pod -n test
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/hello NodePort 10.100.0.30 <none> 5000:30050/TCP 2m
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/hello-84695987b6-l2rkh 1/1 Running 0 2m
참고
https://www.jenkins.io/doc/book/installing/kubernetes/
Kubernetes
This section describes how to use a set of YAML (Yet Another Markup Language) files to install Jenkins on a Kubernetes cluster. The YAML files are easily tracked, edited, and can be reused indefinitely. Create Jenkins deployment file Copy the contents here
www.jenkins.io
'Kubernetes > devops' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Tekton을 이용한 CI/CD (0) | 2022.09.12 |
|---|---|
| Jenkins와 Keycloak을 이용한 OIDC 연동 (0) | 2022.09.10 |
| Nginx Ingress를 통해 Canary 배포 설정 (0) | 2022.09.04 |
| Keptn (활용) (0) | 2022.08.04 |
| Ketpn (설치) (0) | 2022.07.28 |




